AI Quick Prompt
Intro
In generative AI, prompts serve as crucial tools to direct the AI's output. Clear and effective instructions ensure that the output aligns with the user’s needs.
Quick prompts are integrated into workflows for easy access, allowing users to execute pre-defined actions effortlessly. These types of prompts are crafted by experts known as prompt engineers, who focus on the efficiency of AI.
This article discusses the usage of quick prompts.
For more information on all types of prompt patterns, see Designing Effective AI Prompts.
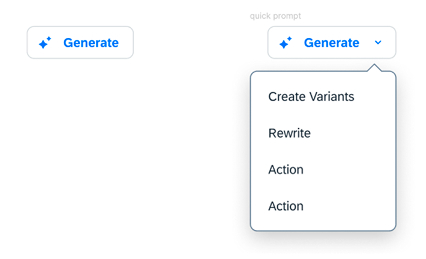
Usage
Do:
- When tasks are repetitive or for common actions within a workflow.
- When input options may be limited in mobile scenarios.
- When the system can only assist with specific actions.
- When users lack expertise in the subject matter.
- When it’s crucial to minimize any bias introduced by users’ writing prompts.
- When maintaining consistent and predictable outcomes is essential.
Don’t:
- When a user’s intent is unpredictable.
- When users need more flexibility in directing the output of the AI model.
- When providing non-AI-related actions is necessary. In this case, offer a dedicated menu button solely for such items.
Behavior and Interaction
Content Generation
Clicking the AI button initiates content generation with AI. As the generation process begins, the AI button transforms to the Stop Generating button, enabling users to stop generation at any time (please see AI Progress Indicator). Primary actions, if there is any, are disabled until generation is complete, preventing users from accessing partially generated content.
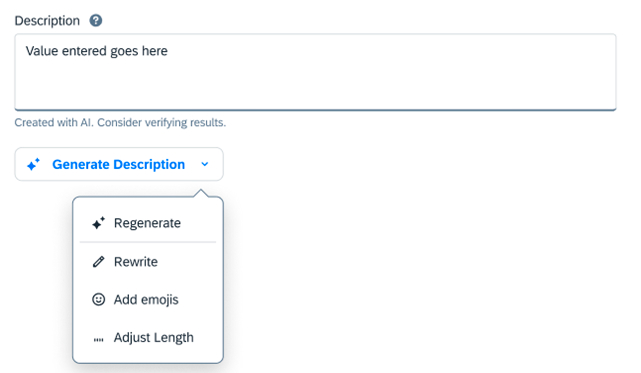
Fine-Tuning
Once the generation process is completed or stopped by the user, the Stop Generating button transitions to an AI menu button. This menu provides a variety of appropriate AI actions as quick prompts that users can apply to all or some of the generated content.
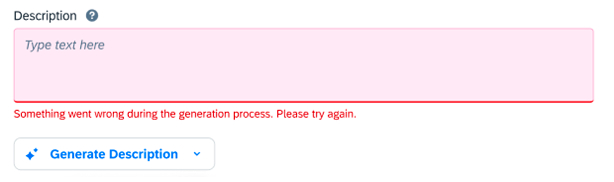
Handling Errors
If the quick prompt is interrupted or fails, follow the guidance for error messages in the message handling article.
For consistent user experiences, we suggest using the following error message:
Something went wrong during the generation process. Please try again.
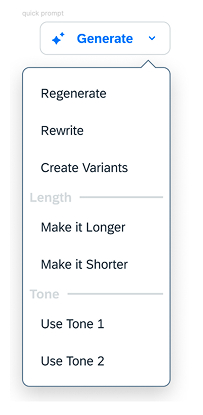
Grouping
If necessary, organize prompts into submenus for easier navigation and to minimize visual clutter. Group quick prompts based on their purpose or the task they build upon.
Prioritize the most essential actions by placing them at the top of each group. Keep group sizes manageable by breaking them down into smaller subgroups to prevent users from feeling overwhelmed by too many options within a single group.
Example submenus:
- Rewrite Text
- Simplify
- Expand
- Rephrase
- Summarize
- Change Tone
- Make More Casual
- Make More Professional
- Adjust Length
- Shorten Text
- Lengthen Text
- Translate
- Language 1
- Language 2
- ...
Terminology
Adhere to the default labels provided below for text generation scenarios. We strongly recommend maintaining consistency and familiarity for users by following the suggested wording. Only make changes to the default text if absolutely necessary for your specific use case.
If you find yourself in this situation, please reach out to the AI Experience team for further guidance.
Standard AI action labels for AI text generation and transformation:
AI Button Labels:
- Generate: Create or produce something, such as text using AI.
- Revise: Change or alter existing content or data using AI.
Submenu Labels:
- Rewrite Text: Changes the structure of the text.
- Change Tone: Adjusts the style or emotional quality of text.
- Adjust Length: Changes the length of text.
- Translate: Convert content or data from one language to another using AI.
AI Action Labels for Menu:
- Fix Spelling and Grammar: Corrects errors in spelling and grammar using AI.
- Simplify Text: Makes text easier to understand with AI.
- Expand: Elaborates on the content, providing more detail or depth.
- Rephrase: Rewrites text to convey the same meaning.
- Summarize: Condenses information while retaining the key points.
- Make More Casual: Makes writing less formal.
- Make More Professional: Makes writing more formal.
- Shorten Text: Reduce the length of the text or data using AI.
- Lengthen Text: Increase the length of the text or data using AI.
- Make Bulleted List: Organizes information into a list format.
- Explain Content: Clarify the meaning of content or data using AI.
Best Practices
For actions not covered above, apply the following guidelines:
- Use a verb in the imperative.
- Keep AI action labels as short as possible while prioritizing clarity for users.
- Use the same AI action labels consistently.
Responsible AI
Appropriate Use of Quick Prompts
Quick prompts are designed to make interactions easier by providing clear, predefined options. This helps users get things done faster and reduces confusion. However, it’s essential to use them in the right situations. They should align with the user’s needs. Quick prompts might be insufficient in complex scenarios where more context or detail is needed. Instead, guided or custom prompts may lead to more accurate and comprehensive responses.
Additionally, ensure that using quick prompts aligns with SAP’s commitment to responsible AI practices and adheres to our SAP Global AI Ethics Policy by completing the AI Ethics Assessment Process. For use cases classified as standard, we recommend completing the AI Ethics Policy Self-Assessment.
User Autonomy
Empower users by giving them the choice to disable quick prompts and AI features in their workflow. Ensure alternative methods are available for users to complete their tasks without relying on AI.
AI Transparency
Ensure clarity in the deployment of quick prompts, making their use and purpose transparent to users. Use clear indicators, like AI icons or buttons, to ensure users know when they’re interacting with AI. Follow our design guidelines to maintain consistency in how these features are presented.
Prevent Bias in Prompt Design
Ensure the prompt design process actively involves measures to prevent bias. Like biased training data, poorly designed prompts can produce skewed or harmful results.
Advocate for a diverse group of users and technical experts to focus on thoughtful prompt design, conduct comprehensive evaluations of user needs and outcomes, and iterate to guarantee that AI-generated content remains bias-free. Their feedback can influence design decisions or the evaluation process.
Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering is the process of designing and refining instructions to guide the behavior and output of generative AI models.
Your product team is responsible for engineering top-notch prompts tailored to the foundation models or large language models (LLMs), guaranteeing that users achieve the desired results when utilizing your AI feature with quick prompts.
Follow the best practices and, where necessary, employ advanced LLM techniques like embeddings and fine-tuning to get the best outcomes.
Helpful Terms
Foundation models
Deep learning models trained on large volumes of unlabeled data using self-supervised learning. Applicable to a wide range of tasks.
Large language models (LLMs)
Deep learning models trained on massive amounts of unlabeled data using self-supervised learning. They excel at understanding and generating natural language for a wide range of tasks.
Prompt engineering
The process of designing and refining instructions to guide the behavior and output of generative AI models.
Embeddings
Embeddings enhance prompts by searching a knowledge base for context, providing a semantic representation of relevant documents, and improving the LLM’s ability to find semantically similar information.
Fine-tuning
Fine-tuning LLMs is the resource-intensive process of customizing a pre-trained language model on specific tasks or datasets to make it more proficient and accurate in generating relevant text.
<e-dropdown data-markup-content="Generate" data-dropdown-align="auto" data-markup-class="e-btn e-btn-dropdown">
<div class="e-dropdown__content">
<div class="e-dropdown__item" href="#">
<a href="#">
<e-icon icon="ai" type="table"></e-icon>
Regenerate
</a>
</div>
<div class="e-dropdown__item e-dropdown__item-righticon" href="#">
<div class="float-right">
</div>
<a href="#">
<e-icon icon="edit" type="table"></e-icon>
Rewrite
</a>
</div>
<div class="e-dropdown__item e-dropdown__item-righticon" href="#">
<div class="float-right">
</div>
<a href="#">
<e-icon icon="smile" type="table"></e-icon>
Add Emoji
</a>
</div>
<div class="e-dropdown__item e-dropdown__item-righticon" href="#">
<div class="float-right">
</div>
<a href="#">
<e-icon icon="expand" type="table"></e-icon>
Adjust Length
</a>
</div>
</div>
</e-dropdown>